Pulse Primer


The Trigger for Root Growth & Nodulation
ANALYSIS (10% CA)
What is It?
- Seed dressing for application onto pulse seed (peas, lentils, chickpeas, … ).
- Calcium-based seed dressing.
- Rhizobia-friendly formulation.
- The Gel Rheology Technology™ keeps the highly concentrated product suspended and helps with seed adhesion and drying out.
- The product is available in 10L jugs, 450L and 1000L IBC’s.
When & Why Use It?
- When seeding into wet and cold conditions or when the top soil is dry.
- Low pH soils, heavy manure land, soils with high Nitrogen levels.
- Sandy and light-textured soils.
- Heavy textured soil with high Mg content.
What to Expect?
- Early emergence and a better stand.
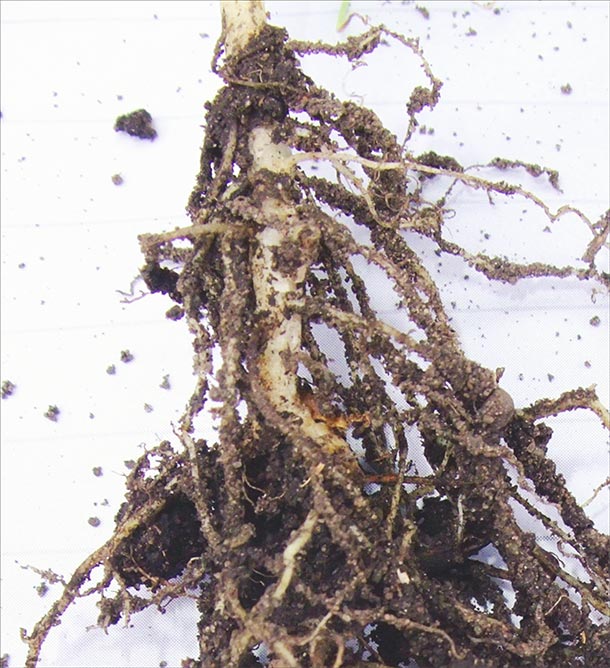
- Extensive root growth.
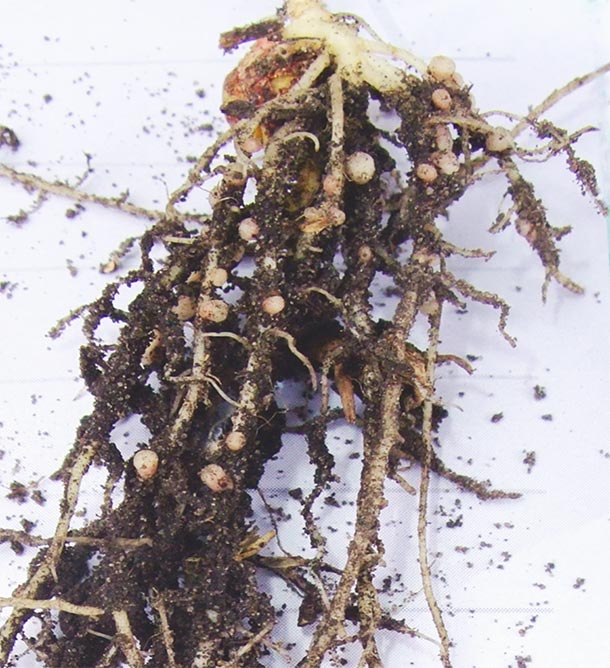
- Better nodulation.
- Better Nitrogen use efficiency and preservation of yield.
Size Options
Tote

10L
Application Guidelines
- Pulse crops: 3 mL/Kg of seed.
- Pulse Primer can be used alone or in combination with seed treatments, dry and liquid inoculants. Check the best option for your targeted combination (see compatibility charts).
- Pulse Primer can be diluted with water for a more uniform coverage onto the seed.
Findings
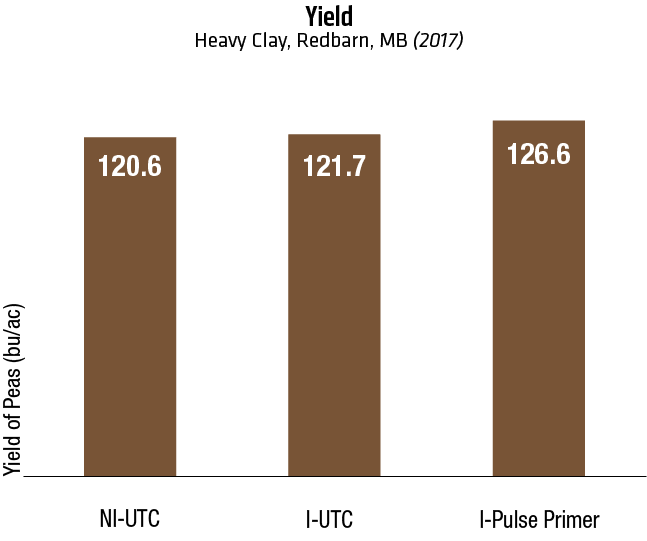
2017 Heavy clay – Manitoba
Saskatchewan
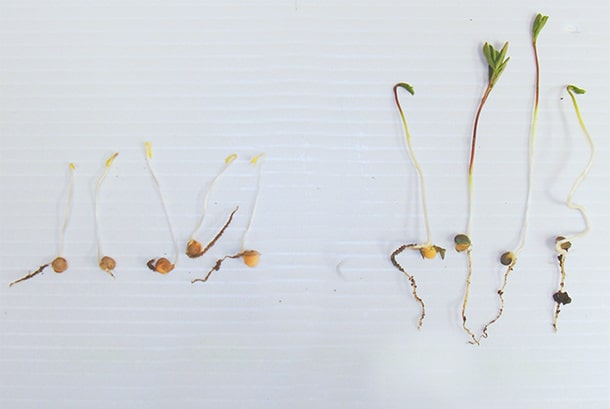

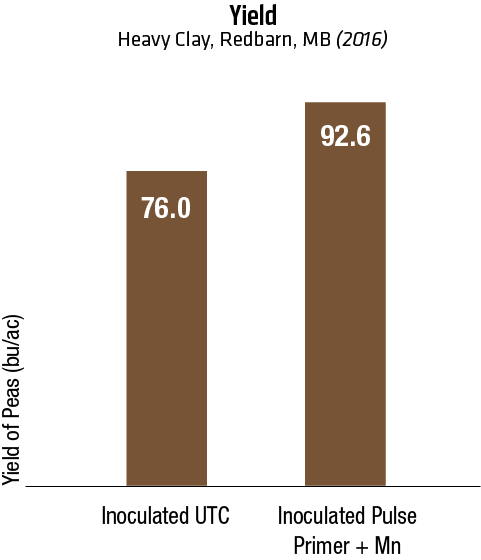
2016 Heavy clay – Manitoba
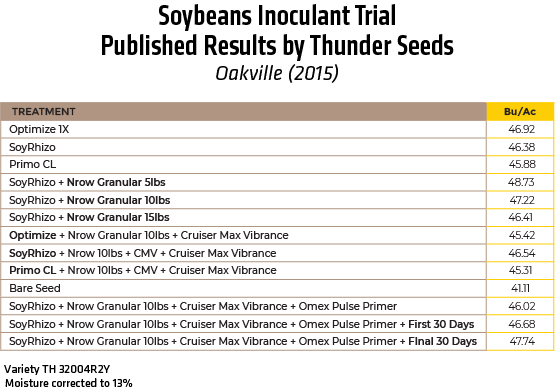
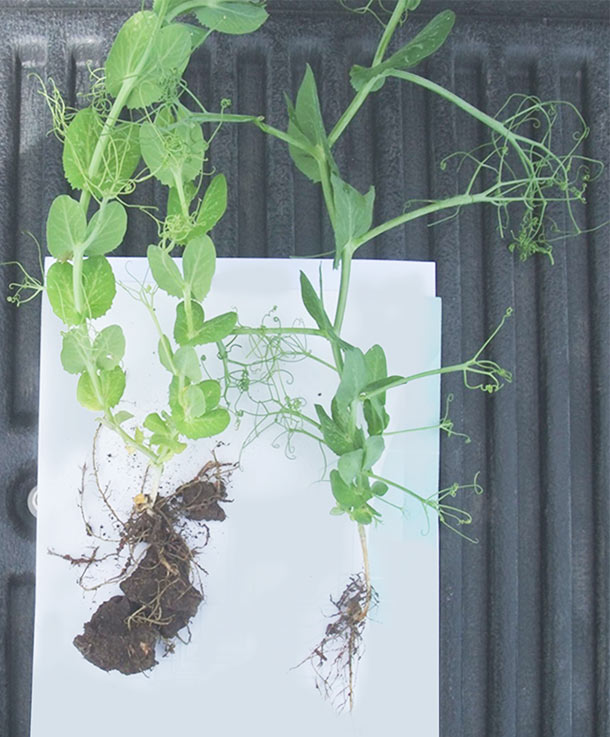
2015
2014 Provost, Alberta

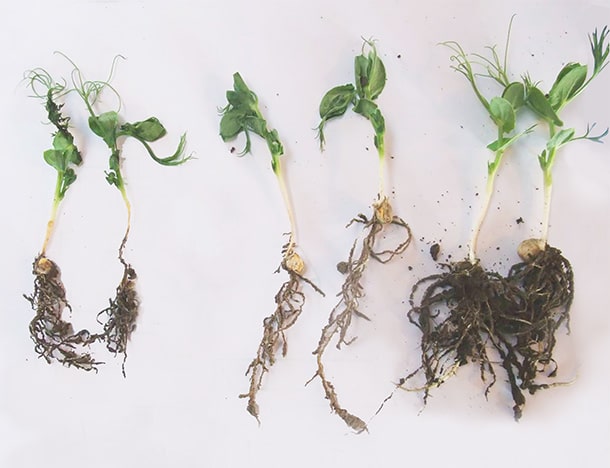
2010 Southern Alberta

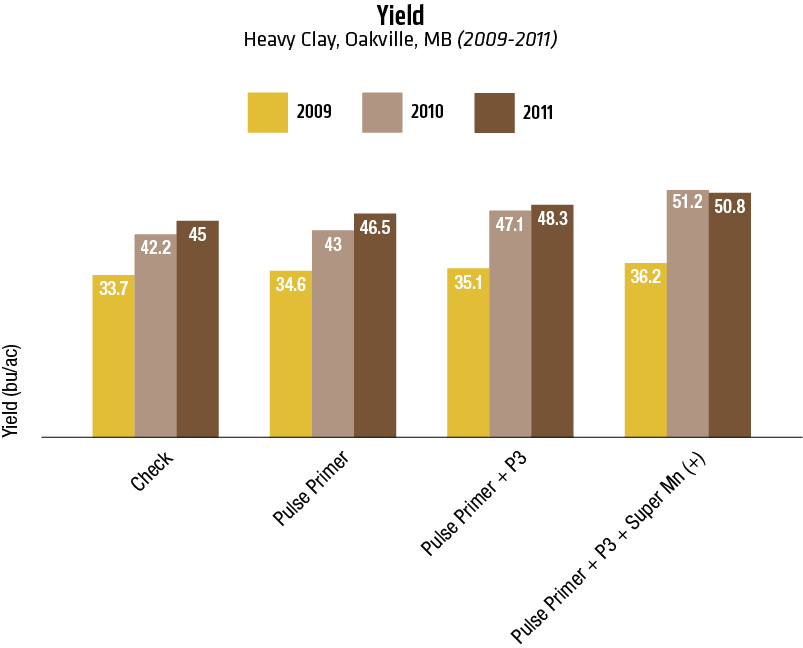
ADDITIONAL Provost, Alberta





